This post is a continuation in our series on data aware storage. In our previous post we looked at what data aware storage is and why it matters. Now let's look at what goes in to making it work.
The Elements That Make Up Data Awareness
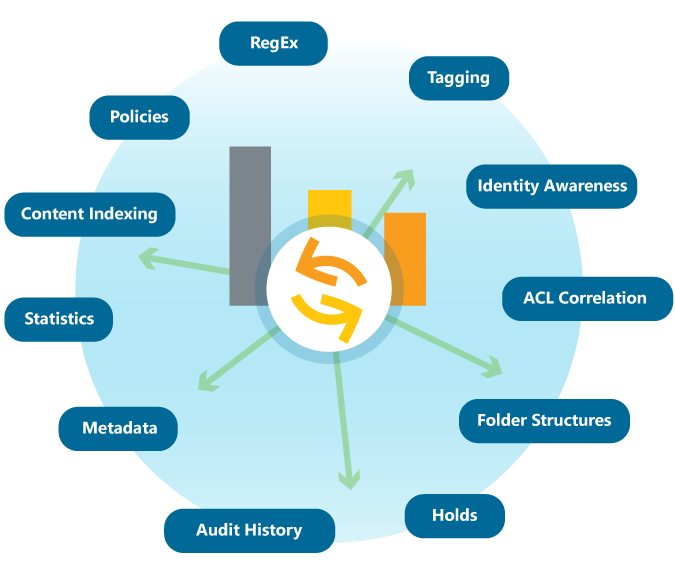
We can't speak for what goes into the mix of other data aware storage vendors, so we'll have to show you things from a HubStor perspective. The following diagram shows you what goes into the HubStor data aware storage mix:
Identity Awareness
A key element of data awareness is that it has an understanding of users and groups. This requires directory synchronization and some background work to map user identities to the access control lists (ACLs) on items and folders. Don't worry, it's fully automated - you don't have to do a thing.
Data Classification
Data classification is the categorization of your information. It can involve identifying what contains private and sensitive information, such as credit card numbers. It can also be as basic as grouping information by content type or age or whether it is relevant to active eDiscovery cases or not. Some classifications in HubStor are default, but we'll explore below how object storage pools can be configured in HubStor for custom classifications as well.
Auditing
Having in-depth knowledge of user activities has become an essential capability for compliance in many industries. Activity intelligence generates audit histories that show us things like which users viewed a particular item of interest and what actions a target user did recently. We'll talk more about the auditing aspect in our upcoming post on what data aware storage offers for security and compliance.
Policies
We also include a data-aware policy engine (patent pending) that evaluates rules and applies actions on a near-real time basis in the cloud. The policies are data aware because they can leverage aspects of our data aware storage as policy criteria and also because each policy automatically maintains its own analytics. We'll spend more time in our next post looking specifically at the data aware policy engine.
Now that we understand some of the key elements of data aware storage, let's have an in-depth look at the underlying object storage framework and how it can be configured custom data classification and content-optimized data awareness.
Data Aware Object Storage Pools
HubStor is an object storage platform with a flexible metadata model that is easily content-optimized for particular unstructured data workloads. Content-optimization allows high-value metadata, including any custom fields, to be handled in special ways, making things like analytics, policy, and search more specific to your particular storage workload(s).
In HubStor, each object storage pool is referred to as a ‘Stor’. HubStor allows you to easily scale-out multiple object storage pools. For geographically distributed environments multiple Stors can be created across multiple StorSites (think of StorSites as datacenter regions) - all seamlessly federated by HubStor for central data awareness, administration, governance, security, and search.
The metadata configuration of each Stor can be configured as follows:
- Required Metadata – If checked, HubStor’s cloud-integrated storage service (the HubStor Connector Service (HCS)) will force any connectors writing to the particular Stor to provide this metadata.
- Persist in DB – If checked, the metadata field can be used for criteria in any of the Stor’s policies.[/list_item]
- Full Text Index – If checked, the metadata field will be persisted in the search index and made visible in HubStor’s end-user and eDiscovery search interfaces for querying.
- Enable for Event-based Retention – If checked, the metadata field will provide query and trigger support for managing event-based retention.
- Aggregation Buckets – These are customizable value ranges (data classifications) for which statistics will be maintained on the metadata for visual breakdowns in HubStor's dashboards.
So imagine having Stors for legacy email archives and PST files, user file shares, video recordings, genomic research, medical scans, etc. -- Each providing different metadata fields that you can specially call out for tracking, security rules, governance policies, search, reporting, etc.
The following screen shot shows a Stor's metadata configuration. Any of your content's metadata can be configured in this framework.

Conclusion
As you can see, there's a lot of different data points coming together for your storage to be data aware. If this seems complex don't be afraid. The complexity exists only under the hood. As a customer, you don't get bogged down in these details. You simply get the insights and the controls.
Before getting into specific examples showing how data aware storage benefits security, eDiscovery, and IT, in our next post in this data aware storage series we'll be looking at the data aware policy engine.